Notes
Notes and References
Neural Networks
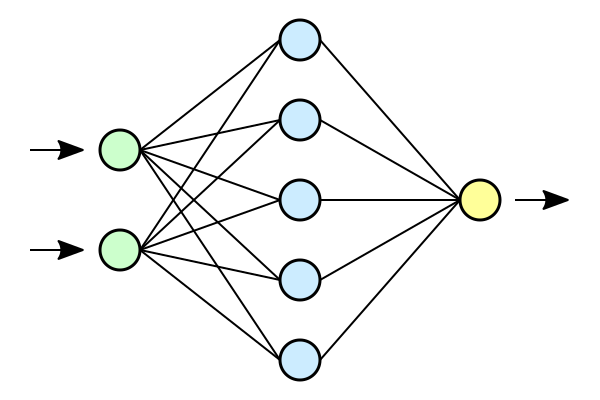
Perceptron:
- A perceptron is a fundamental unit in artificial neural networks (ANNs), acting as a simple mathematical function.
- Denoted as $k$, it processes $m + 1$ inputs ($x_0$ to $x_m$) with corresponding weights ($w_{k0}$ to $w_{km}$).
- The $x_0$ input serves as a bias input with $w_{k0} = b_k$, simplifying the representation.
Perceptron Output:
- The output ($y_k$) of the $k$-th neuron is determined by the transfer function $\varphi$.
- Mathematically, $y_k = \varphi\left(\sum_{j=0}^{m} w_{kj}x_j\right)$.
- The transfer function $\varphi$ introduces non-linearity, allowing neural networks to learn complex patterns.
Neural Network Structure:
- Neural networks consist of layers: an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer.
- The input layer receives initial data, hidden layers process information, and the output layer produces predictions.
- Neurons in each layer are interconnected with weights, which are adjusted during the learning process.
Learning Process:
-
Weights and Gradients Initialization:
- Initialize weights appropriately; improper initialization may lead to slow convergence or convergence to suboptimal solutions.
- Gradients represent the sensitivity of the loss function to changes in weights.
-
Forward Propagation:
- Inputs are fed forward through the network, reaching the output layer.
- Weighted sums of inputs are computed at each neuron, and the transfer function is applied.
- Mathematically, $z_k = \sum_{j=0}^{m} w_{kj}x_j$, and $y_k = \varphi(z_k)$.
-
Output Activation:
- Activation functions introduce non-linearity to the output layer.
- Common activation functions include sigmoid ($\sigma$), tanh, and ReLU.
- Mathematically, $a_k = \varphi(z_k)$, where $a_k$ is the activated output.
-
Loss Calculation:
- Compare the predicted output to the actual output using a loss function.
- The loss quantifies the disparity between predictions and ground truth.
- For example, Mean Squared Error (MSE) is often used: $L = \frac{1}{2}(a_k - y_{\text{true}})^2$.
-
Backward Propagation and Weight Update:
- Gradients are calculated using the chain rule during backpropagation.
- Weights are updated using gradient descent to minimize the loss.
- Mathematically, $\frac{\partial L}{\partial w_{kj}} = \frac{\partial L}{\partial a_k} \cdot \frac{\partial a_k}{\partial z_k} \cdot \frac{\partial z_k}{\partial w_{kj}}$.
- Update rule: $w_{kj} \leftarrow w_{kj} - \alpha \frac{\partial L}{\partial w_{kj}}$, where $\alpha$ is the learning rate.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Perceptron:
def __init__(self, input_size, learning_rate=0.01):
self.weights = np.random.rand(input_size + 1)
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
def activation_function(self, x):
return 1 if x >= 0 else 0
def predict(self, inputs):
inputs = np.insert(inputs, 0, 1) # Insert bias term
summation = np.dot(self.weights, inputs)
return self.activation_function(summation)
def train(self, inputs, target):
prediction = self.predict(inputs)
error = target - prediction
inputs = np.insert(inputs, 0, 1) # Insert bias term
self.weights += self.learning_rate * error * inputs
class PerceptronLayer:
def __init__(self, input_size, num_neurons, learning_rate=0.01):
self.perceptrons = [Perceptron(input_size, learning_rate) for _ in range(num_neurons)]
def predict(self, inputs):
return np.array([perceptron.predict(inputs) for perceptron in self.perceptrons])
def train(self, inputs, target):
for perceptron, target_value in zip(self.perceptrons, target):
perceptron.train(inputs, target_value)
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, learning_rate=0.01):
self.hidden_layer = PerceptronLayer(input_size, hidden_size, learning_rate)
self.output_layer = PerceptronLayer(hidden_size, output_size, learning_rate)
def train(self, inputs, target):
hidden_output = self.hidden_layer.predict(inputs)
self.output_layer.train(hidden_output, target)
def predict(self, inputs):
hidden_output = self.hidden_layer.predict(inputs)
return self.output_layer.predict(hidden_output)
def plot_decision_boundary(network, x_range, y_range):
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_range[0], x_range[1], 100), np.linspace(y_range[0], y_range[1], 100))
predictions = np.array([network.predict(np.array([x, y])) for x, y in zip(xx.ravel(), yy.ravel())])
predictions = predictions.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, predictions, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral, alpha=0.8)
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], c=labels, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Example usage for XOR problem
data = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
labels = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0])
input_size = 2
hidden_size = 4
output_size = 1
nn = NeuralNetwork(input_size, hidden_size, output_size, learning_rate=0.1)
# Train the neural network
for epoch in range(10000):
for example, label in zip(data, labels):
nn.train(example, label)
# Plot decision boundary
plot_decision_boundary(nn, [0, 1], [0, 1])
More complex example
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
class Perceptron:
def __init__(self, input_size, learning_rate=0.01):
self.weights = np.random.rand(input_size + 1)
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
def relu(self, x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
def softmax(self, x):
exp_values = np.exp(x - np.max(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True))
return exp_values / np.sum(exp_values, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
def predict(self, inputs):
inputs = np.insert(inputs, 0, 1) # Insert bias term
hidden_output = self.relu(np.dot(self.weights, inputs))
return self.softmax(hidden_output)
def train(self, inputs, target):
prediction = self.predict(inputs)
error = target - prediction
inputs = np.insert(inputs, 0, 1) # Insert bias term
gradient = np.dot(error, inputs)
self.weights += self.learning_rate * gradient
class PerceptronLayer:
def __init__(self, input_size, num_neurons, learning_rate=0.01):
self.perceptrons = [Perceptron(input_size, learning_rate) for _ in range(num_neurons)]
def predict(self, inputs):
return np.array([perceptron.predict(inputs) for perceptron in self.perceptrons])
def train(self, inputs, target):
for perceptron, target_value in zip(self.perceptrons, target):
perceptron.train(inputs, target_value)
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, learning_rate=0.01):
self.hidden_layer = PerceptronLayer(input_size, hidden_size, learning_rate)
self.output_layer = PerceptronLayer(hidden_size, output_size, learning_rate)
def train(self, inputs, target):
hidden_output = self.hidden_layer.predict(inputs)
self.output_layer.train(hidden_output, target)
def predict(self, inputs):
hidden_output = self.hidden_layer.predict(inputs)
return self.output_layer.predict(hidden_output)
def one_hot_encode(labels, num_classes):
one_hot_labels = np.zeros((len(labels), num_classes))
one_hot_labels[np.arange(len(labels)), labels] = 1
return one_hot_labels
def plot_decision_boundary(network, data, labels, title):
h = .02
x_min, x_max = data[:, 0].min() - 1, data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = data[:, 1].min() - 1, data[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = np.argmax(np.array([network.predict(np.array([x, y])) for x, y in zip(xx.ravel(), yy.ravel())]), axis=1)
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral, alpha=0.8)
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], c=labels, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
def main():
# Load Iris dataset
iris = datasets.load_iris()
data = iris.data[:, :2] # Use only the first two features for simplicity
labels = iris.target
# Standardize the features
scaler = StandardScaler()
data = scaler.fit_transform(data)
# Split the dataset into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
num_classes = len(np.unique(labels))
y_train_encoded = one_hot_encode(y_train, num_classes)
input_size = X_train.shape[1]
hidden_size = 8
output_size = num_classes
nn = NeuralNetwork(input_size, hidden_size, output_size, learning_rate=0.01)
# Train the neural network
for epoch in range(5000):
for example, label in zip(X_train, y_train_encoded):
nn.train(example, label)
# Make predictions on the test set
y_pred_encoded = np.array([nn.predict(example) for example in X_test])
y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred_encoded, axis=1)
# Evaluate accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
# Plot decision boundary
plot_decision_boundary(nn, X_test, y_test, "Decision Boundary for Iris Classification")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()